Running & Configuring Python venv3 in Linux
Jul 24, 2025 2-3 min read Article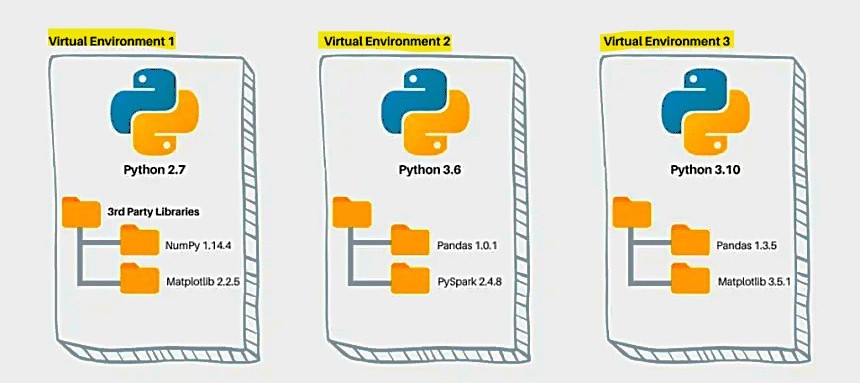
What is Python venv ??
A Python virtual environment (venv) is a tool that helps you create a separate space for each of your Python projects. This space includes its own version of Python and its own set of packages (libraries).
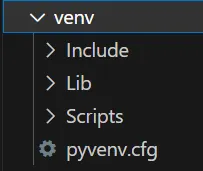
A virtual environment (venv) is simply a directory with a specific file structure, containing a Python interpreter and directories for installed packages.
Using venv avoids conflicts between projects, especially when different projects need different versions of the same library. It's like having a clean, self-contained workspace for every project. The venv module is built into Python, so you don't need to install anything extra to use it. When we activate a venv, it modifies the environment variables to prioritize the venv's directories, ensuring that the correct Python interpreter and packages are used, instead of the global ones.Directories ( folders ) within a Venv 👇
Real-Life Analogy
Imagine you're a chef working in a large Indian wedding catering service. You have to cook for multiple weddings happening on the same day:
- Each wedding has its own menu, ingredients, and cooking style (North Indian, South Indian, Jain, etc.).
- If you use the same kitchen (global environment) for all weddings, you might mix up ingredients—someone’s Jain menu might accidentally get garlic or onion!
- So, instead, you set up separate kitchens (venvs) for each wedding, with only the specific ingredients and tools needed for that menu.
- That way, there’s no confusion or mixing up, and every wedding gets exactly what it needs.
In the same way, Python virtual environments make sure each project has exactly what it needs, without interfering with others.
Install Python venv3
Install py venv using apt:
sudo apt update && sudo apt install python3-venvor using pyenv:
curl https://pyenv.run | bashCreate a Virtual Environment
Navigate to your desired directory and run:
python3 -m venv env_name
( env_name is the name of your virtual environment directory )Activate the Virtual Environment
source env_name/bin/activate (Bash shell)
For other shells:
source env_name/bin/activate.fish (fish shell)source env_name/bin/activate.csh (csh shell)Deactivate the Virtual Environment
Just by running the folllowing command inside the venv:
deactivateDelete the Virtual Environment
We can delete the Venv by command:
rm -rf env_nameUsage Example
- Installation:
sudo apt install python3-venv(done) - Creating venv directory:
python3 -m venv py_venv - Activating:
source py_venv/bin/activate(successfully running) - Deactivating:
deactivate(successfully stopped)
